The 4-C's
COLOR
A truly colorless diamond is extremely rare. Most diamonds possess varying degrees of yellow or brown and even faint color nuances can make a substantial difference in value. If a diamond is well cut, the diamond's refraction and dispersion often will disguise certain degrees of coloration. To accurately and consistently grade color, an accredited experienced Diamond grader will utilize special lighting to compare the diamond being graded to a set of Master Color Comparison Diamonds which have met exacting standards of cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
Color Grading systems have been standardized and the below examples represent the grading methods used by one of North Americas most respected Gemological laboratories. Diamonds in the “Z+” range known as Fancy color diamonds can occur in almost any color or shade including yellow, orange, brown, blue, green, pink and, very rarely, red. These stones are usually darker in tone or saturation than Z on the GIA grading scale. They are graded according to the intensity of their color and are extremely rare and command top market price.
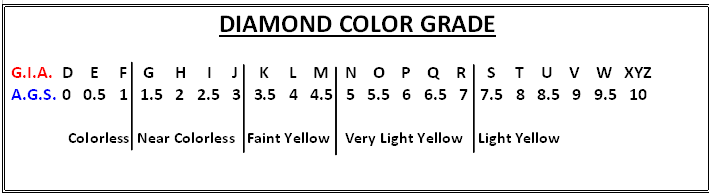
COLOR grading standards used by the Gemological Institute of America and American Gem Society

A collection of Fancy shaped and Fancy colored Diamonds

CUT
Diamonds have a unique ability to manipulate light efficiently maximized only by cutting and polishing the diamond to an extremely high level of accuracy. Of all the 4 Cs, cut has the greatest effect on a diamond's beauty. In grading, cut evaluates the Diamond cutters skill. The proportions of a diamond and its overall symmetry and polish will determine how:
the light is refracted to show off the diamonds' brilliance (the total light reflected from a diamond),
it brings out the diamond's fire (the dispersion of light into the colors of the spectrum),
and scintillation (the flashes of light, or sparkle, when a diamond is moved).
Proportions is the relationships between table size, crown angle and pavilion depth.
Symmetry refers to the precision with which the facets of a diamond are aligned with each other and the consistency of facet shape and size per given section.
Polish refers to the degree of "polishing lines" that appear on the surface of a finished diamond caused by the tiny diamond crystals which are embedded in the polishing wheels used by the diamond cutters to polish the surface of the diamond.
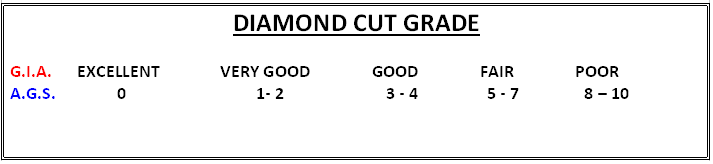
CUT grading standards used by the Gemological Institute of America and American Gem Society

CLARITY
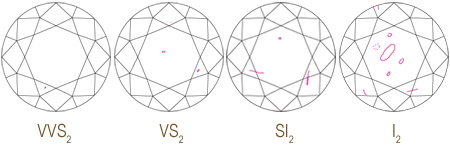
Clarity is the evaluation of a diamond's unique birthmarks called inclusions (internal) and blemishes (external). The fewer inclusions or blemishes make the diamond rarer and more desirable. To locate these tiny characteristics, an accredited Gemologist will evaluate the Diamond under 10x magnification taking into consideration the size, nature, position, color or relief, and quantity of clarity characteristics when assigning a Clarity grade.
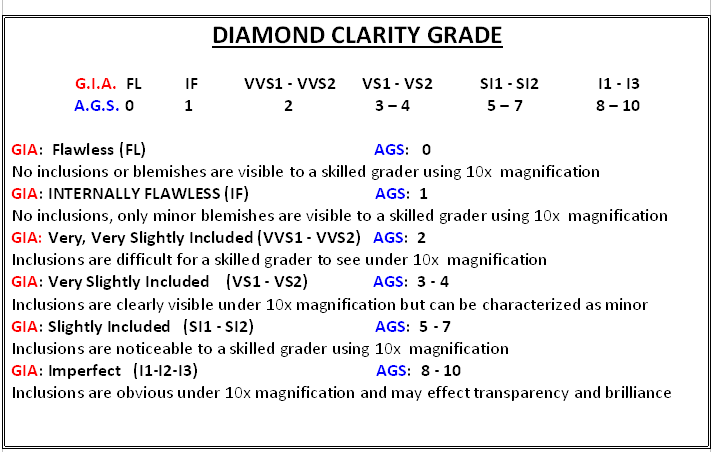
CLARITY grading standards used by the Gemological Institute of America and American Gem Society
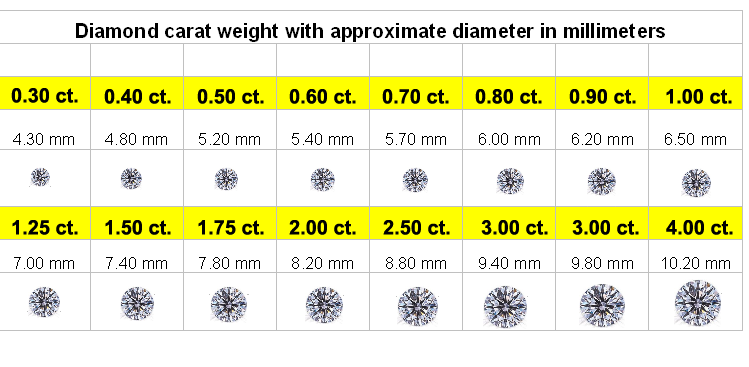
CARAT
In the past, gem traders used the carob seed in their scales to assess the weight of diamonds and other gemstones. The humble seed gained prominence for its fairly uniform weight and
since is now known as the carat, the standard used to measure diamond weight.
Each carat is further divided into points, each point representing 1/100th of a carat, so 100 points = 1.00 carat. While weight may be the least important of the four Cs in determining value, it may be the easiest of the four Cs to accurately gauge and is the most objective. As diamonds increase in size, their cost tends to increase. Thus, a one-carat diamond may cost more than twice as much as a one-half carat stone of equal quality. Weight does not always enhance the value of a diamond. In fact, when a diamond is improperly cut, added weight may serve only to reduce its brilliance.
DIAMOND is derived from the ancient Greek word "adamas', unbreakable and has a grade of 10 on the Mohs Scale of Mineral Hardness, making it the hardest natural material known.